If you polled a class of kindergartners today and asked them what they want to do when they grow up, it’s doubtful that any of them would say “data entry.” However, many adults nonetheless spend hours entering data and performing other mind-numbing tasks.
Fortunately, technology has evolved to the point that humans no longer need to devote their days to repetitive labor. Instead, they can delegate it to robotic process automation (RPA) software.
With the development of RPA solutions, businesses can now let bots take over mundane activities, allowing human employees to focus on strategic projects. Overall, there’s incredible potential to boost productivity and efficiency while driving organizational growth.
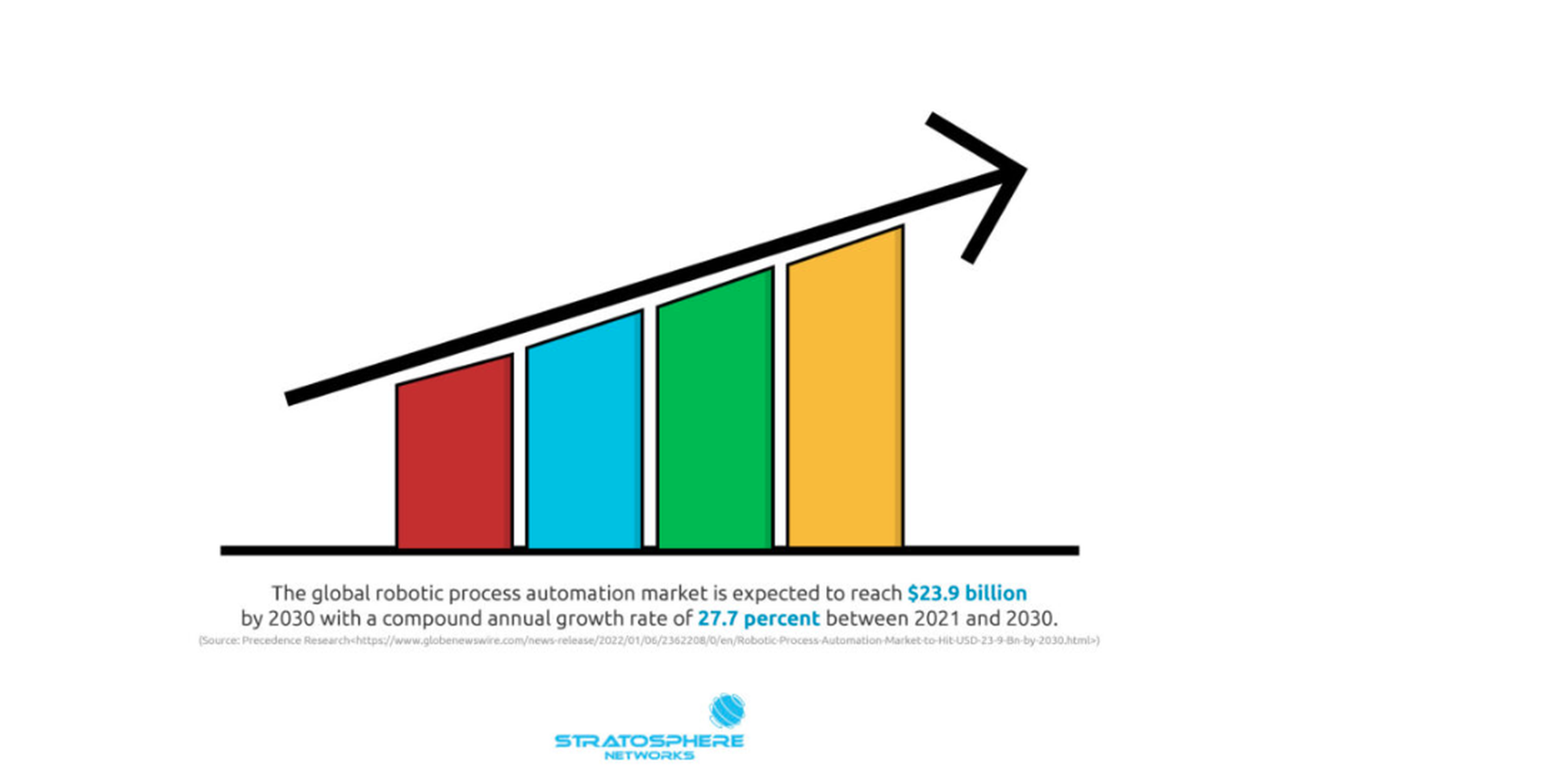
Subsequently, RPA solutions are becoming increasingly popular: The global robotic process automation market is expected to reach $23.9 billion by 2030 with a compound annual growth rate of 27.7 percent between 2021 and 2030, according to Precedence Research.
If you’re a business leader who’s curious about robotic process automation and what the technology can potentially do for your company, this guide provides a high-level overview of what RPA is, how it functions, and the benefits and potential disadvantages of implementing it.
How Robotic Process Automation Works
With RPA solutions, you can create and manage software robots that interface with applications and systems in a way that duplicates human workers’ actions, according to UiPath, a global robotic process automation software company. The bots can carry out various tasks, including interpreting what’s on a screen and extracting and inputting data. RPA software tools can either wholly or partially automate rule-based, manual and repetitive tasks, according to the Association for Intelligent Information Management (AIIM). The technology can efficiently tackle high-volume, low-complexity work such as the following:
- Data entry
- Order tracking
- Employee on- and off-boarding
- Accounts payable invoice processing
- Simple customer service inquiry responses (e.g., password resets)
- Compliance reporting
- Tax estimates
- Processing payment applications
- And more
RPA has various use cases, according to IBM. For example, insurers might deploy this technology to speed up claims processing and underwriting. In the healthcare industry, providers might implement RPA for information management or prescription management, among other tedious assignments. Meanwhile, in the retail world, bots can handle obligations such as fraud detection and order management.
RPA Pros and Cons
The Pros of RPA
Like any technology, robotic process automation software has its potential advantages and drawbacks.
On the plus side, RPA solutions can help your organization achieve the following, according to IBM, UiPath and the AIIM:
- Increased accuracy and speed since robots can complete simple tasks faster and with greater precision than humans
- Reduced costs due to higher productivity and ROI for human workers who are free to focus on higher-priority projects
- Faster digital transformation and increased innovation as staff members focus more on long-term strategy
- Improved employee engagement and satisfaction due to the elimination of tedious labor
The Cons of RPA
On the other hand, IBM explains RPA solutions also have their limitations and possible issues with adoption.
- Enterprises can run into problems scaling RPA solutions because of internal and regulatory updates.
- Because RPA can reduce or eliminate the need for certain types of labor while creating potential for new roles, implementing the technology can necessitate significant organizational changes, and employees might have trouble adjusting. Comprehensive training and communication about shifting priorities are essential.
Ultimately, you’ll need to carefully consider your short- and long-term needs, issues and objectives to determine whether RPA implementation is the right decision for your business.
Contributed blog courtesy of Stratosphere Networks and authored by Kevin Rubin, president and CIO at Stratosphere Networks. Read more contributed blogs from Stratosphere Networks here.




